Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Scientists Discover A New Way To Treat HIV
Know about a new way to treat HIV here in this article, check it out.
HIV/AIDS is still considered a taboo in certain parts of the world. If you are infected with HIV you are ostracized from the society. This feeling itself tend to affect the patient mentally and many a times patients go into depression.
There are various treatment options available for HIV/AIDS that are specifically directed towards the treatment of symptoms.
Well, working towards this effect, in what can be called as one of the outstanding discoveries, scientists have found a treasure trove of microorganisms with potential to treat HIV in Chile's Atacama Desert, one of the highest and driest places on Earth.
For the study, researchers have taken soil samples from heights of 3,000 to 5,000 metres above sea level. Michael Goodfellow, from the Newcastle University in the UK, said the study focused on actinobacteria as they are keystone species in our ecosystems and are acknowledged as an unrivalled source of bioactive compounds.
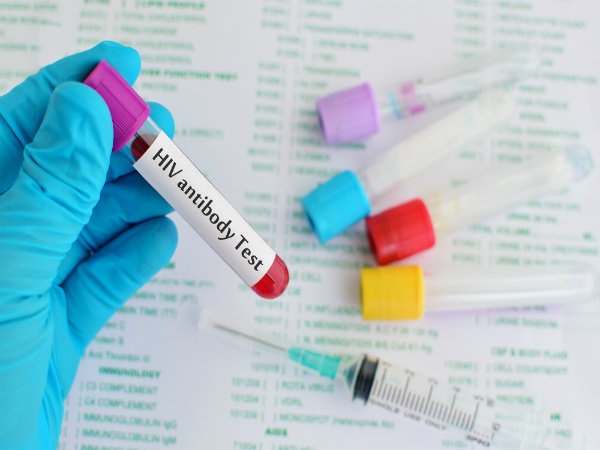
During the course of the study, the researchers found that this landscape is an extraordinary repository for actinobacterial 'dark matter' - which comprises the vast majority of microbes that microbiologists are currently unable to cultivate.
The researchers found that 40 per cent of the actinobacteria captured in samples could not be given ascribed names as they had never before been discovered. "This microbial seed bank represents an enormous untapped resource for biotechnology programmes, especially in an era where resistance to existing antibiotics is rapidly becoming a major threat to global health," Goodfellow said.
He said the discovery of new bacteria could potentially be used to create new treatments as work continues to tackle the antibiotics problem.
"It is also notable that one strain of bacteria found is proven to be an inhibitor of an enzyme that allows the HIV virus to reproduce itself. This could provide essential clues for the development of anti-HIV drugs," Goodfellow said.
The study was recently published in the journal Extremophiles.

What Is HIV & How Does It Transmit?
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, which is our body's natural defence against illness. So when the immune system gets weak, then someone living with HIV, who is not receiving treatment, will find it harder and harder to fight off infections and diseases.
The virus can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen or vaginal fluids. Fever, fatigue and sore throat are a few of the initial symptoms of HIV. If treated on time then one can prevent it from progressing it to AIDS.
In case of AIDS, strict adherence to antiretroviral regimens (ARVs) can slow the disease's progress as well as prevent secondary infections and complications.
(With Agency Inputs)



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












