Latest Updates
-
 International Human Solidarity Day 2025: History, Significance, and Why It Matters
International Human Solidarity Day 2025: History, Significance, and Why It Matters -
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
World Radiography Day: Types, Purpose And Procedure Of X-ray Imaging
World Radiography Day is celebrated every year on 8 November to mark the invention of X-ray by Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895. X-ray is one of the common imaging tests suggested by a medical expert to get a view of the internal body parts in a non-invasive way. The procedure helps to diagnose certain medical conditions and defects like infection, breakage, swelling and others.
To carry out the X-ray, a medical expert sends X-ray beams through the patient's body and record the result in the form of images on a fluorescent screen. [1]
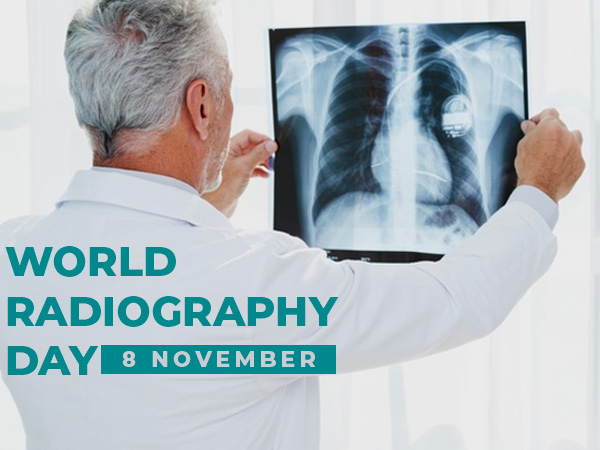
When the X-ray beams pass through the body, they get absorbed by different parts depending on its density. For example, muscles or fat will show up in grey, bones (or any dense material) will show up in white and air (especially in the lungs) will be seen in black colour. Likewise, any defect in the body part is diagnosed with the help of an X-ray.
Types Of X-ray Imaging
X-ray examination is carried out in different forms depending on the medical condition of an individual.
- Fluoroscopy: Mainly used to see the movement of the body part like a heartbeat, digestive process or clogged arteries [2]
- Mammography: To detect signs of breast cancer [3]
- Computed tomography (CT) scans: This is done to detect injuries related to the brain, tumours and abnormalities of blood vessels. Here, images from different body angles are taken and combined in a computer to create a detailed cross-sectional view. [4]
Purpose Of X-ray Imaging
X-ray is used to identify a defect in body parts, especially in diagnosing medical conditions like the following:
- Bone-related issues like osteoporosis, arthritis or bone fractures [1]
- Problems related to cavities or tooth decay
- Tumours of the bones [5]
- Lung infection, lung cancer and tuberculosis
- Gastrointestinal problems [6]
- Breast cancer [3]
- Kidney stones [7]
- An enlarged heart or blood flow in the heart
- Swallowed objects and many more. [8]
Why Is X-ray Imaging Test Popular?
- When compared to other tests, it has no or minimal side effects.
- The X-ray process does not take much time.
- The electromagnetic radiation does not remain in the patient's body once the X-ray imaging is completed.
- It is widely available in all hospitals, clinics, ambulances and nursing homes as it is inexpensive.
- It is the easiest and painless way to diagnose an underlying medical condition.
How Is X-ray Imaging Performed?
The procedure for X-ray examination involves the following steps:
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- An X-ray expert may ask you first to remove clothing or any jewellery placed in the body part which is to be examined. [9]
- Then they will tell you the position in which you have to lie down so that the affected body part can completely come in contact with the X-ray beam.
- If the X-ray needs to be performed in the lower body part (near the reproductive organs), they will cover them with a lead apron as it stops all the electromagnetic beams and does not harm the sensitive organs. [10]
- They may ask you to hold the breath to get a clear image as breathing may cause the image to be blurry.
- When the X-ray needs to be performed with a contrast agent, the medical expert will give you the instructions beforehand so that you can come prepared.
- If a contrast agent is injected, first they will observe the patient for any possible side effects (like itching, nausea) and then carry out the imaging process. [11]
- After the procedure, the doctor will check your report and accordingly order for additional tests or suggest medications.
- [1] Chen, H., Rogalski, M. M., & Anker, J. N. (2012). Advances in functional X-ray imaging techniques and contrast agents. Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP, 14(39), 13469–13486. doi:10.1039/c2cp41858d
- [2] Miller, D. L. (2008). Overview of contemporary interventional fluoroscopy procedures. Health physics, 95(5), 638-644.
- [3] Løberg, M., Lousdal, M. L., Bretthauer, M., & Kalager, M. (2015). Benefits and harms of mammography screening. Breast cancer research : BCR, 17(1), 63. doi:10.1186/s13058-015-0525-z
- [4] Power, S. P., Moloney, F., Twomey, M., James, K., O'Connor, O. J., & Maher, M. M. (2016). Computed tomography and patient risk: Facts, perceptions and uncertainties. World journal of radiology, 8(12), 902–915. doi:10.4329/wjr.v8.i12.902
- [5] Kuleta-Bosak, E., Kluczewska, E., Machnik-Broncel, J., Madziara, W., Ciupińska-Kajor, M., Sojka, D., … Wilk, R. (2010). Suitability of imaging methods (X-ray, CT, MRI) in the diagnostics of Ewing's sarcoma in children - analysis of own material. Polish journal of radiology, 75(1), 18–28.
- [6] Gilja, O. H., Hatlebakk, J. G., Odegaard, S., Berstad, A., Viola, I., Giertsen, C., … Gregersen, H. (2007). Advanced imaging and visualization in gastrointestinal disorders. World journal of gastroenterology, 13(9), 1408–1421. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1408
- [7] Brisbane, W., Bailey, M. R., & Sorensen, M. D. (2016). An overview of kidney stone imaging techniques. Nature reviews. Urology, 13(11), 654–662. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2016.154
- [8] Saps, M., Rosen, J. M., & Ecanow, J. (2014). X-ray detection of ingested non-metallic foreign bodies. World journal of clinical pediatrics, 3(2), 14–18. doi:10.5409/wjcp.v3.i2.14
- [9] Liang, H., Flint, D. J., & Benson, B. W. (2011). Why should we insist patients remove all jewellery?. Dento maxillo facial radiology, 40(5), 328–330. doi:10.1259/dmfr/77333052
- [10] Fawcett, S. L., Gomez, A. C., Barter, S. J., Ditchfield, M., & Set, P. (2012). More harm than good? The anatomy of misguided shielding of the ovaries. The British journal of radiology, 85(1016), e442–e447. doi:10.1259/bjr/25742247
- [11] Andreucci, M., Solomon, R., & Tasanarong, A. (2014). Side effects of radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors, and prevention. BioMed research international, 2014, 741018. doi:10.1155/2014/741018



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












