Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
HIV Vaccine Awareness Day 2020: Steps To Prevent HIV/AIDS
Every year on 18 May HIV Vaccine Awareness Day (HVAD) is observed to recognise the volunteers, health professionals, community members and scientists who are working together to develop a safe and effective vaccine to prevent HIV. The day also aims to educate communities about the importance of preventive HIV vaccine research.
As per the World Health Organization (WHO) at the end of the year 2018, 37.9 million people were living with HIV worldwide. And around 0.8 per cent of adults aged between 15 to 49 years are living with HIV [1].

HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that infects and destroys CD4 cells, also called T-cells, which are white blood cells that act as the body's natural defence system against various pathogens and infections. HIV is responsible for causing AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), a chronic, life-threatening condition.
HIV is primarily transmitted through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, breast milk, vaginal fluids, pre-seminal fluids and rectal fluids. HIV is a lifelong condition and there is no cure for it currently, although scientists around the world are working to develop a HIV vaccine.
However, taking certain steps can help prevent the transmission of HIV. Read on to know.
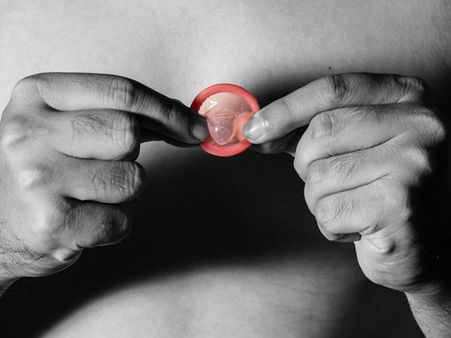
1. Practice safe sex
One of the most effective ways of preventing HIV is to practice safe sex by using condoms and dental dams (it is a thin piece of latex used between the mouth, vagina or anus during oral sex) whenever you have oral, vaginal or anal sex. Consistent and correct usage of condoms is highly effective in preventing HIV infection [2].
According to a study published in the journal Social Science and Medicine, condoms are 90 to 95 per cent effective when it is used regularly. And individuals who use condoms consistently are 10 to 20 times at a lesser risk of getting infected when exposed to the virus as compared to individuals who don't use condoms regularly [3].

2. Limit the number of sexual partners
Individuals who have unprotected sex with multiple sexual partners are a greater risk of contracting HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
A study showed that Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest rate of HIV and STIs due to multiple sexual partners, untreated STIs, poverty, lack of male circumcision and migration [4].
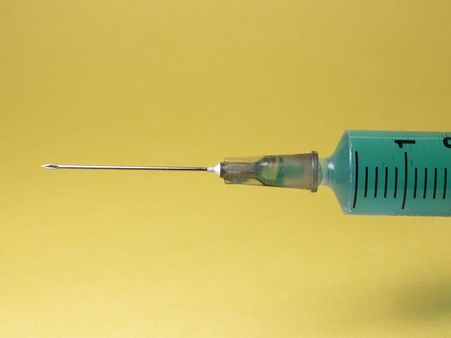
3. Avoid sharing needles or syringes
People who use needles or syringes to inject drugs for medical purposes, for tattoos and piercings and any other purposes should avoid sharing their needles with anyone to lower the risk of contracting or getting HIV/AIDS.

4. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEp)
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEp) is a pill considered to be highly effective for preventing HIV. If taken daily, it lowers the risk of contracting HIV infection through sexual contact by 99 per cent and for people who inject drugs, PrEp reduces HIV risk by 74 per cent.
PrEp is for people who don't have HIV but who are at an increased risk of getting HIV. If a person is exposed to the virus through sexual contact or usage of injection drugs, having this pill can take hold of the virus and prevent it from spreading throughout the body [5].
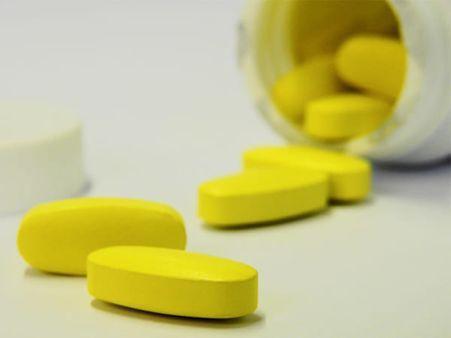
5. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) involves taking antiretroviral medicines (ART) after a possible exposure to HIV to prevent the virus from spreading throughout your body. PEP should be taken within 72 hours after you were exposed to the virus, otherwise, it won't work. It should be used in emergency situations and is not for regular use by people who may be exposed to the virus frequently.
If used correctly PEP is considered effective in preventing HIV, but not 100 per cent, according to the CDC [6].
To Conclude...
As HIV continues to be a major global health public issue and the numbers continue to rise among the population, it is important to protect yourself from contracting or transmitting HIV by following the above methods.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












