Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
10 Serious Complications Of Coronavirus Infection You Need To Know
The researchers and scientists are still studying the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to identify what kind of complications it has on a person who is infected by the virus.
As per a January 2020 study finding, infected patients who were mostly men were 49-years-old and had complications like acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute cardiac injury, secondary infection and RNAaemia [1].

Researchers have been stressing on the fact that people with underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, heart and lung disease are at a higher risk of getting coronavirus leading to complications, which may be life-threatening. However, people without any pre-existing health conditions are at a risk of getting the complications too.
Here we have compiled a list of coronavirus complications.
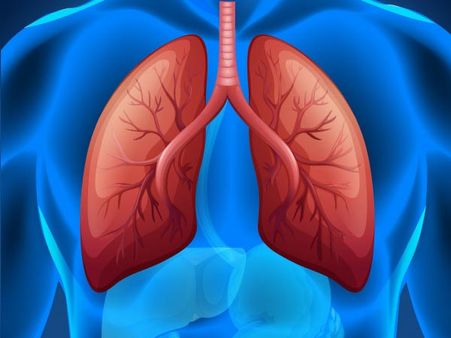
1. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is one of the most common complications of coronavirus. It occurs when fluid builds up in the air sacs (alveoli) in your lungs. The build-up of fluid prevents your lungs from filling with enough oxygen causing insufficient oxygen circulation in your bloodstream and other organs, thereby making your body deprived of oxygen [2]. This causes difficulty in breathing and the patient may require a ventilator to breathe to aid in the recovery process.
2. Pneumonia
Another serious complication of coronavirus is pneumonia, an infection which occurs in one or both the lungs. The infection causes inflammation in the air sacs of your lungs, making it difficult for you to breathe.
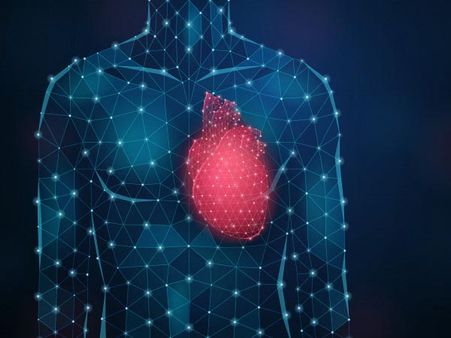
3. Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia occurs when electrical impulses in the heart work improperly causing your heart to beat either too quickly, too slow or with an irregular pattern. Many patients with COVID-19 suffered from arrhythmia and other heart problems. However, it is not clear whether the coronavirus affects the patient's heart directly or if it occurs due to the COVID-19 illness causing stress on the heart [3].
4. Sepsis
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that is caused when the body responds to an infection. When the body naturally releases the chemicals into the bloodstream to fight the infection, it can trigger inflammation in the body leading to the damage of multiple organs. In severe cases, sepsis can lead to septic shock.
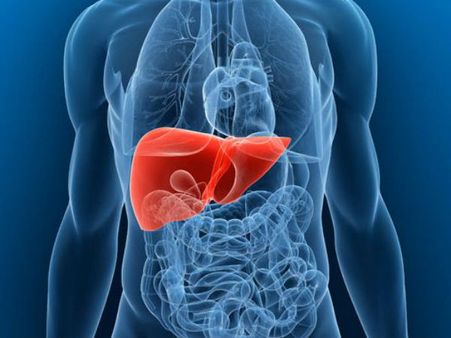
5. Acute liver injury
Acute liver injury and liver failure are life-threatening complications of coronavirus. It happens when the viral infection attacks the liver cells and it tends to occur in severe cases of COVID-19 [4].
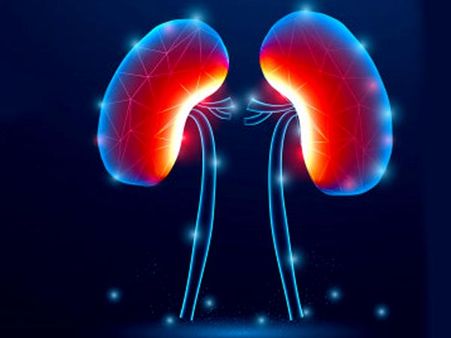
6. Acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury occurs when there is a build-up of waste products in the blood making it hard for your kidneys to maintain the right balance of fluid in the body. Dialysis is given for the kidneys to function properly and to maintain the right amount of fluid in the blood.
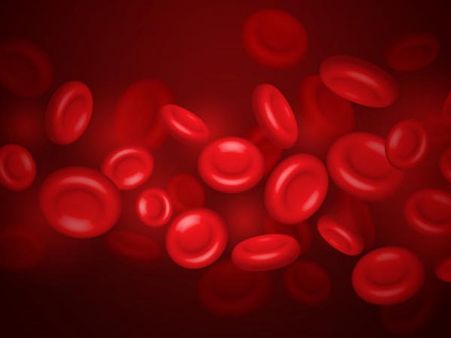
7. Disseminated intravascular coagulation
It
is
a
serious
condition
in
which
small
blood
clots
develop
in
the
bloodstream,
blocking
the
small
blood
vessels.
As
a
result,
there
is
a
reduction
in
the
blood
flow
and
the
blood
is
unable
to
reach
the
organs.
When
the
condition
progresses,
the
platelets
and
clotting
factors,
the
substances
that
are
responsible
for
forming
blood
clots
are
used
up
and
it
can
eventually
lead
to
excessive
bleeding.
Coagulation
disorders
have
been
seen
in
patients
with
COVID-19
[5].
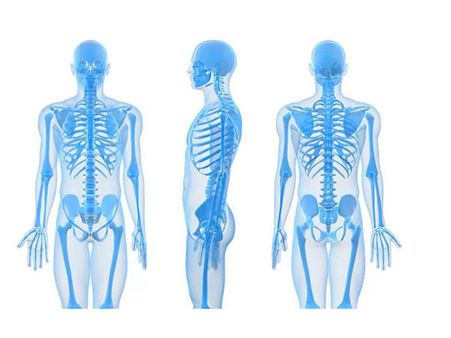
8. Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis occurs when there is a breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle tissues. This leads to the release of a protein (myoglobin) into the blood. Excess of myoglobin in the blood can cause kidney damage [6].

9. Secondary infection
Secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after the treatment of the previous infection, which is unrelated to the first infection you had. In the case of COVID-19, a person can get secondary infection if he/she has been exposed to a viral or bacterial infection while the patient is fighting against or recovering from the COVID-19 illness [7].

10. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is the bleeding that can either happen in the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. The bleeding comes out from the stomach and oesophagus and the level of bleeding may range from mild to severe which can be life-threatening [8].



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












