Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Stuttering: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
In order to deliver the right information, one must be able to speak clearly and fluently. When a person has trouble speaking in a fluid, or flowing way, for example, he/she may say the whole word or parts of the word more than once, or pause awkwardly between words - it is termed as stuttering.
A speech disorder, it is also called as stammering or diffluent speech. Stuttering usually develops between the age of 2 and 6 years old [1] .
Many children go through normal periods of dysfluency lasting for around 6 months and as the child's development progresses, the stuttering will stop. Dysfluencies lasting longer than this may need intervention. Stuttering can even be seen during adolescence or adulthood [2] .
Types Of Stuttering
The speech disorder is classified into three different types and they are as follows [3] :
Developmental

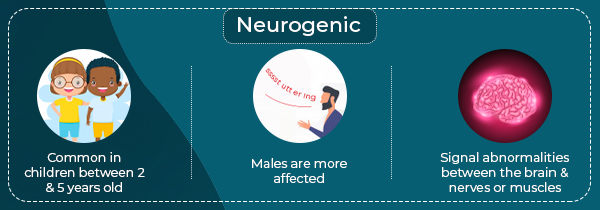
Neurogenic
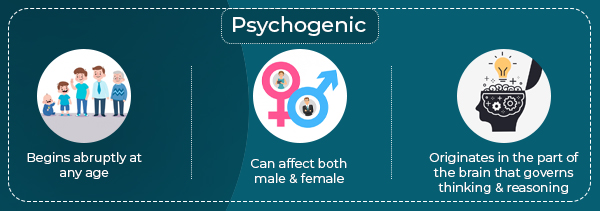
Psychogenic
Symptoms Of Stuttering
Stuttering is characterised by repeated words, sounds, or syllables, halting speech production and uneven rate of speech [4] .
Other signs that indicate the speech disorder are as follows:
- Frustration when attempting to communicate
- Refusal to speak
-
Hesitation
or
pausing
before
starting
to
speak
Using extra sounds or words into sentences, such as 'uh' or 'mm' - Facial tics
- Lip tremors
- Excessive blinking of eyes
- Tension in the face and upper body
- Repetition of words or phrases
- Head jerks
- Clenching fists
Causes Of Stuttering
There is no specific cause for the speech disorder. However, the probable causes are as follows [5] :

- Family history of stuttering
- Development during childhood
- Neurophysiology
- Family dynamics
- Being in contact with another stutter
- Abnormalities in speech motor control
Apart from the aforementioned, neurogenic stuttering can be caused by brain injuries and severe emotional trauma can cause psychogenic stuttering [6] .
Diagnosis Of Stuttering
If your child or someone you know stutters, you should get help from a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP), as early as possible. Because, it is important to intervene children or adults with stuttering at the earliest, as it not only affects the way a person speaks but also nurtures feelings like fear, shame, avoidance, isolation anxiety, guilt etc. Hence early intervention has faster progress and helps to reduce its negative consequences [7] .
There is no requirement for invasive testing.
Treatment For Stuttering
Not everyone who stutters will require treatment because developmental stuttering usually resolves with time. The medical and emotional care provided for individuals with stuttering is as follows [8] [9] :
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- Speech therapy: It can help interruptions in speech and improve one's self-confidence. Therapy focuses on controlling speech patterns by monitoring the rate of speech, breath support, and laryngeal tension.
- Electronic devices: Various electronic devices are available to enhance fluency.
- Parent-child interaction: Parental involvement in practising techniques at home is a critical step in improving the child's stuttering.
- Cognitive behavioural therapy: This type of psychotherapy can help you learn to identify and change ways of thinking that might make stuttering worse. This therapy is also beneficial for managing the related stress, anxiety and self-esteem problems [10] .
Do's And Dont's For Parents & Caregivers
- Don't finish their sentences: As a parent or teacher or even a listener you might be tempted to finish their sentences to help them but this does more harm than good.
- Don't look distressed or avoid eye contact: You need to let the person know by your manner that you are paying attention and listening to what they say rather how they say it.
- Don't say, relax, or slowdown: Such simple advice can be demeaning to them.
- Don't speak deliberately too slow or too fast: Talking naturally promotes good communication model.
- Provide an opportunity to talk: You need to allow them to speak without distractions from family members, classmates or friends.
- Be patient: Give them enough time to talk e.g.: give the person time to answer a question before you ask the second one.
- Be aware of their difficulties: Persons with stuttering may have factors that aggravate their difficulty e.g.: telephonic conversation, time pressure, unfamiliar listeners, fatigue or stress.
- Repeat or rephrase: You can repeat or rephrase what the person says that you have understood it.
With inputs from Rekha D, Speech-Language Pathologist
- [1] Yairi, E., & Seery, C. H. (2015). Stuttering: Foundations and clinical applications. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
- [2] Ward, D. (2017). Stuttering and cluttering: frameworks for understanding and treatment. Psychology Press.
- [3] Guitar, B. (2018). Stuttering. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- [4] Packman, A., & Attanasio, J. S. (2017). Theoretical issues in stuttering. Routledge.
- [5] O’Brian, S., Carey, B., Lowe, R., Onslow, M., Packman, A., & Cream, A. (2016). The Camperdown Program stuttering treatment guide. Australian Stuttering Research Centre.
- [6] Andrews, G., Howie, P. M., Dozsa, M., & Guitar, B. E. (1982). Stuttering: Speech pattern characteristics under fluency-inducing conditions. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 25(2), 208-216.
- [7] Mozaffarilegha, M., Namazi, H., Tahaei, A. A., & Jafari, S. (2019). Complexity-based analysis of the difference between normal subjects and subjects with stuttering in speech evoked auditory brainstem response. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 39(4), 490-497.
- [8] Davidow, J. H., Grossman, H. L., & Edge, R. L. (2019). Stuttering Frequency, Speech Rate, Speech Naturalness, and Speech Effort During the Production of Voluntary Stuttering. Language and speech, 62(2), 318-332.
- [9] Sander, R. W., & Osborne, C. A. (2019). Stuttering: Understanding and Treating a Common Disability. American Family Physician, 100(9).
- [10] Zamani, P., & Latifi, S. M. (2019). T he efficacy of prolonged speech technique in boys with mild stuttering.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












