Latest Updates
-
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs -
 Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year
Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year -
 As The Last New Moon Of 2025 Approaches, Make A Wish Based On Your Rising Sign
As The Last New Moon Of 2025 Approaches, Make A Wish Based On Your Rising Sign
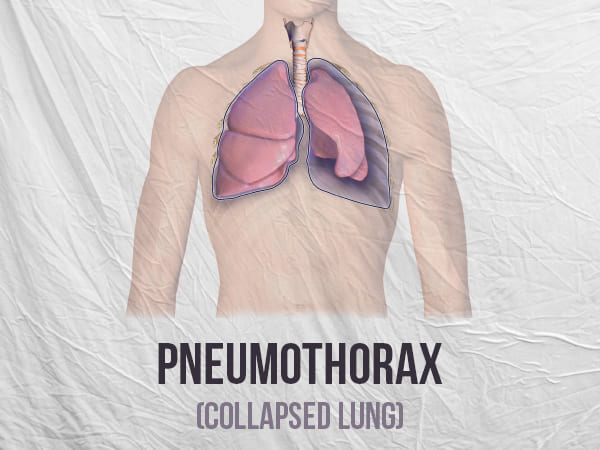
Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung): Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors And Treatments
Collapsed lung, medically termed as pneumothorax, is a condition in which the air leaks into the space between the lung and the chest wall (pleural space) due to open injury or rupture in the tissues of the lung. The leakage of the air outside the lungs disrupt the balance of the pressure of the air inside, leading to the collapse of the lungs. [1]
Pneumothorax causes severe chest pain and shortness of breath. It can also occur without any underlying condition and heal on its own. If the cause is injury or accident, it may cause a life-threatening event. Take a look at the details.

Types Of Pneumothorax
1. Traumatic pneumothorax (TP): Occurs due to injury or trauma in the lungs or chest wall. It includes: [2]
- A bullet shot or stab wound in the chest.
- Vehicle accident
- Fractured rib
- Fall of a heavy object or hard hit on the chest.
- Mountain climbing or scuba diving
- Medical procedures such as mechanical ventilation
- Primary nontraumatic pneumothorax (PNP): Here, collapsed lung occur due to no specific reason or without any preexisting lung condition. It can occur in healthy adults too.
- Secondary nontraumatic pneumothorax (SNP): The main causes of SNP are lung diseases such as COPD, lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, asthma, whooping cough, bacterial pneumonia or cystic fibrosis. SNP is also caused due to cigarette smoking.
2. Nontraumatic pneumothorax (NP): It is not as a result of trauma or injury. NP are of two types: [3]
Causes Of Pneumothorax
When a person breathes in and out, the lungs inflate or say, increase in size till the inner layers of the chest cavity. In the process, the vacuum inside the lungs increases while remains decreased in the pleural space, which is the area outside the lungs but within the chest cavity.
In pneumothorax, a hole or damage is caused in the lung tissues due to injury, trauma or lung diseases. This causes the air inside the lungs to escape into the pleural space. The air that has escaped outside the lungs, now starts to disrupt the balance of the pressure inside the lungs, causing the lungs to contract more instead of inflating, resulting in lung collapse.

Symptoms Of Pneumothorax
- Sharp chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Pain while breathing
- Cough
- Rapid heartbeat and breathing due to more pressure on the heart by the outside lung pressure.
- Bluish skin due to the less supply of oxygen to the tissues
- Fatigue

Risk Factors Of Pneumothorax
- Smoking [4]
- Being thin, tall and between the age 10-30 (People above 40 are more prone to SNP)
- Playing hard sports such as football or hockey
- Being male
- An occupation that involves a change in atmospheric pressure.
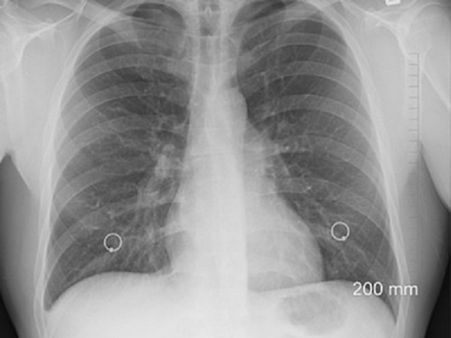
Diagnosis Of Pneumothorax
- Physical examination: Here, the medical expert will ask questions about the history of lung disease, trauma or accident.
- Arterial blood gas test: To measure the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. Low levels of oxygen and high levels of CO2 indicates pneumothorax.
- Imaging tests: It includes a CT scan, ECG or X-ray to confirm pneumothorax.
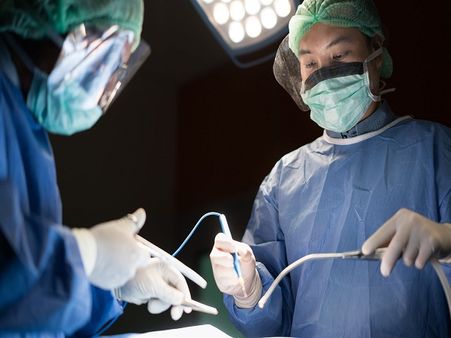
Treatment Of Pneumothorax
If the pneumothorax is caused without any underlying conditions, it may go on its own after a few days as the air gets reabsorbed by the lungs. Severe cases require immediate treatments such as: [5]
- Needle insertion: Here, a hollow needle is inserted in the pleural space to allow excess air to come out. It is a short procedure.
- Chest tube insertion: It is similar to the insertion of a needle in the chest. However, here a chest tube is inserted which is attached to a suction machine to pull out excess air from the pleural space.
- Surgery: If the condition does not improve even after the above two procedures, surgery is carried out in which the leakage in the lung tissues is closed.
- Medications: To reduce chest pain.

How To Prevent Pneumothorax
- Avoid smoking
- Take plenty of rest.
- Consult a medical expert if you notice frequent symptoms of pneumothorax



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications