Latest Updates
-
 International Human Solidarity Day 2025: History, Significance, and Why It Matters
International Human Solidarity Day 2025: History, Significance, and Why It Matters -
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
Muscle Cramps: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis And Treatment
Muscle cramps are sudden involuntary contraction that occurs in one or more muscles. They can be often painful which may happen while exercising, resting or sleeping at night. Muscle cramps are common and usually are seen among the elderly and in young people after a vigorous workout [1].

What Are Muscle Cramps? [2]
A muscle cramp is characterised by a sudden, painful involuntary contraction of a single muscle, entire muscle group or selected muscle fibres. The muscles in the arms and legs are voluntary muscles, which means you can control their movement and they alternately contract and relax. The muscles in the neck, head and trunk work in the same way.
When a muscle or muscle fibre involuntarily contracts, it can lead to muscle cramps. Muscle cramps can last from few minutes to a few seconds depending on the cause.

Causes Of Muscle Cramps
• Exercise associated muscle cramp (EAMC) - It happens during or immediately after an exercise. Exercise associated muscle cramp occurs either due to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance or a transient peripheral neurological disorder. Excessive sweating due to strenuous exercise causes dehydration and loss of electrolytes (magnesium, calcium, potassium and sodium), which leads to muscle cramping [2].
On the other hand, repetitive muscle exercise can cause muscle fatigue which causes an increase in excitatory afferent activity within the muscle spindles and decreases inhibitory afferent activity within the Golgi tendon. All of this leads to altered neuromuscular activity.
• Diabetes - Muscle cramps in diabetic patients have been linked to the presence of neuropathy, with a hyper excitability of the peripheral nerve. Around 60 per cent of type 1 diabetic patients have less muscle cramps as compared to 80 per cent of type 2 diabetic patients. In type 2 diabetes, nephropathy causes muscle cramps [2].
• Nocturnal leg cramps - The exact cause of nocturnal leg cramps is unknown. However, it could be due to certain activities such as when a person stands a lot while working or performing high physical activities during the day. It could also be due to electrolyte imbalance, neurological disorders, hormonal and metabolic disorders or compressed nerve roots or arterial vessels [2].
In addition, consumption of diuretics, beta-blockers, and statins drugs could also be the cause of leg cramps at night. The cramps usually occur in the calf of the leg.
• Leg cramps in pregnant women - Muscle cramps are common in pregnant women and what exactly causes it is unknown. However, it could be due to many factors and these include alterations of neuromuscular function, weight gain, inadequate blood flow to the muscles, muscles of the lower limbs working more, or peripheral nerve compressions [2].
• Writer's cramp - It is a specific type of focal dystonia (involuntary muscle contraction causing repetitive or twisting movements) of the hands which can occur while doing any fine motor movements such as writing. It occurs in people aged between 30 to 50 years [2].
• Cramp-fasciculation syndrome(CFS) - It is a rare condition of the muscles which causes persistent muscle cramping and twitching [2].
• Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) - Muscle cramp is a common symptom of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a disease of the nervous system that weakens the muscles and disables physical functionality. 95 per cent of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis have reported muscle cramps [2].
• Cirrhosis - About 88 per cent of cirrhosis patients experience muscle cramps [2].
• Anti-Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein Antibody (Anti-MAG) Neuropathy - It is a rare disease that causes muscle cramps in 60 per cent of the patients with this condition [2].
• End-stage kidney disease - Patients with chronic kidney failure who are undergoing dialysis can experience muscle cramps due to low magnesium levels in the body [3].

Symptoms Of Muscle Cramps
The most obvious symptom of muscle cramp is a sudden, sharp pain that usually develops in the leg muscles, particularly in the calf. You might feel or see a firm, tender lump of swollen muscle beneath the skin.

Risk Factors Of Muscle Cramps
•
Age
•
Dehydration
•
Pregnancy
•
Medical
Conditions

When To See A Doctor
Muscle cramps usually go away on their own and are rarely serious to seek medical care. However, you should consult a doctor if you experience severe discomfort, swollen leg, redness in the skin, muscle weakness and when they don't improve with self-care.
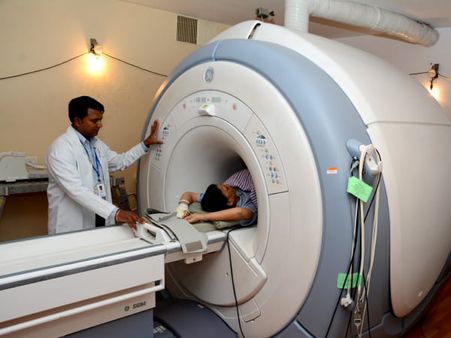
Diagnosis Of Muscle Cramps
The doctor will perform a physical examination and ask questions about the onset of muscle cramps. The doctor may conduct an electromyography (EMG), a diagnostic procedure to check the health of the muscles and the nerve cells that control the motor neurons. Other tests such as MRI or CT scan can rule out any neurological lesions [4].
Treatment Of Muscle Cramps
Self-care measures can treat muscle cramps. In addition, your doctor can show some stretching exercises that can help relax the muscles [4]. And muscle relaxant medications may be prescribed by your doctor to ease muscle cramps if caused by an injury.

Prevention Of Muscle Cramps
•
Do
warm-up
exercises
before
starting
any
exercise
as
it
will
help
reduce
the
muscle
strain.
•
Avoid
exercising
immediately
after
eating
meals.
•
Reduce
the
intake
of
caffeinated
beverages
•
Drink
plenty
of
water
to
prevent
dehydration.
•
Eat
calcium
and
potassium-rich
foods.
Common FAQs
Q. How do you get rid of muscle cramps fast?
A. Stretch and massage the cramped muscle and apply cold or warm water compress on the affected muscles.
Q. What is the best vitamin for leg cramps?
A. Increase the intake of magnesium to reduce the risk of muscle cramps.
Q. What is the best natural muscle relaxer?
A. Chamomile, cherry juice, magnesium, vitamin D, cayenne pepper and blueberry smoothies are some of the best natural muscle relaxers.
Q. How can I stop my legs from cramping at night?
A. Stretch your legs, drink plenty of water, change your sleeping position, avoid sleeping on a heavy bedding and wear the right footwear.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












