Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
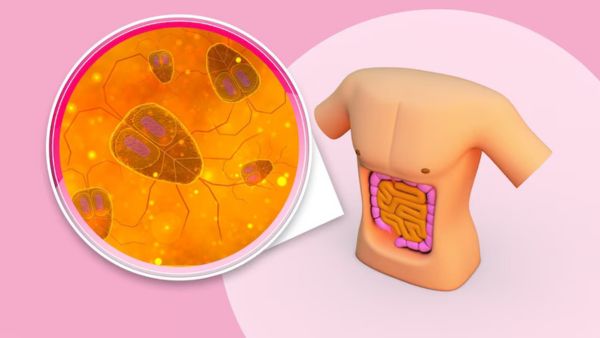
How To Know If You Have Diarrhoea Or Dysentery?
Diarrhoea and dysentery are two common gastrointestinal conditions that can cause discomfort and distress. While these two may share some similarities, it is important to understand the key differences between the two.

In this article, we will look at the differences between diarrhoea and dysentery, so the next time you'll know which one you have and can take the appropriate measures.
Take a look.
How To Know If You Have Diarrhoea Or Dysentery?
1. Stool consistency
Diarrhoea: Frequent loose, watery stools.
Dysentery: Blood or mucus may be present in the stool, accompanied by abdominal pain.
2. Frequency of bowel movements
Diarrhoea: Three or more bowel movements in a day.
Dysentery: Fewer bowel movements than usual, with a persistent urge to pass stool.
3. Abdominal cramps and pain
Diarrhoea: Mild to moderate abdominal cramps may occur.
Dysentery: Severe abdominal pain and cramps are common.
4. Fever
Diarrhoea: Occasional low-grade fever.
Dysentery: High fever, often accompanied by chills.
5. Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhoea: Nausea and vomiting may occur, but it is less common.
Dysentery: Nausea and vomiting are more common, along with a loss of appetite.

Prevention Tips
- Practice good hygiene, including regular handwashing.
- Avoid consuming contaminated food or water.
- Ensure food is properly cooked and stored.
- Stay hydrated by drinking clean water and fluids.
- Get vaccinated against diseases that can cause diarrhoea or dysentery.
When To Seek Medical Help?
- Persistent symptoms that worsen or do not improve.
- Signs of dehydration, such as excessive thirst, dry mouth, or decreased urine output.
- Presence of blood or mucus in the stool.
- High fever or severe abdominal pain.
- Symptoms in young children, elderly, or individuals with weakened immune systems.
On A Final Note...
Knowing the difference between diarrhoea and dysentery is crucial for appropriate management and treatment.
While mild cases can often be managed at home with home remedies, it is important to seek medical help if symptoms persist or worsen. By practising good hygiene and taking preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing these gastrointestinal conditions.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












