Latest Updates
-
 Do You Know How Christmas Trees Became A Holiday Tradition And The Meaning Behind Their Decorations?
Do You Know How Christmas Trees Became A Holiday Tradition And The Meaning Behind Their Decorations? -
 Why Every Family Has a ‘Constantly Tired’ Member: Expert Explains The Hidden Epidemic of Energy Deficiency
Why Every Family Has a ‘Constantly Tired’ Member: Expert Explains The Hidden Epidemic of Energy Deficiency -
 Christmas 2025: Your Go-To Christmas Movie Watchlist for the Holidays
Christmas 2025: Your Go-To Christmas Movie Watchlist for the Holidays -
 Are Heavy Winter Creams Clogging Your Pores? Find Out From The Expert
Are Heavy Winter Creams Clogging Your Pores? Find Out From The Expert -
 Christmas 2025: Banks, Markets, Schools, Transport — What’s Open And Closed In India On December 25th
Christmas 2025: Banks, Markets, Schools, Transport — What’s Open And Closed In India On December 25th -
 Kisan Diwas 2025: The Story Behind National Farmers Day, Know Key Government Schemes This Year
Kisan Diwas 2025: The Story Behind National Farmers Day, Know Key Government Schemes This Year -
 Happy Birthday Ahaan Panday: The ‘Saiyaara’ Star Who Assisted On ‘Rock On 2’, Nearly Debuted With Ajay Devgn
Happy Birthday Ahaan Panday: The ‘Saiyaara’ Star Who Assisted On ‘Rock On 2’, Nearly Debuted With Ajay Devgn -
 Weekly Career Horoscope 23–28 December 2025: Aries! Year-End Efforts Bring Recognition And Clarity
Weekly Career Horoscope 23–28 December 2025: Aries! Year-End Efforts Bring Recognition And Clarity -
 Weekly Love Horoscope 23–28 December 2025: Virgo! Letting Go Of Control Improves Your Love Life
Weekly Love Horoscope 23–28 December 2025: Virgo! Letting Go Of Control Improves Your Love Life -
 Year Ender 2025: The Top 10 Best Local Food Cities In The World, Amchi Mumbai Makes It To The List Too!
Year Ender 2025: The Top 10 Best Local Food Cities In The World, Amchi Mumbai Makes It To The List Too!
Does Diabetes Weaken Your Teeth? What Is The Sweet Truth?
Your sweet tooth can also make you lose a tooth! Does diabetes weaken your teeth? Yes, it jolly well does. Diabetes teeth and gum problems aren't a new fact, but what's sad is that they are a potentially vicious cycle. Diabetes has countless effects, poor dental health being one of them.
And if you ask, "Can poor oral health lead to diabetes?" the answer is yes! Prolonged dental infections can raise your blood sugar levels and delay diabetes management. India, the "diabetes capital of the world," needs to awaken soon to fight this plague called diabetes.
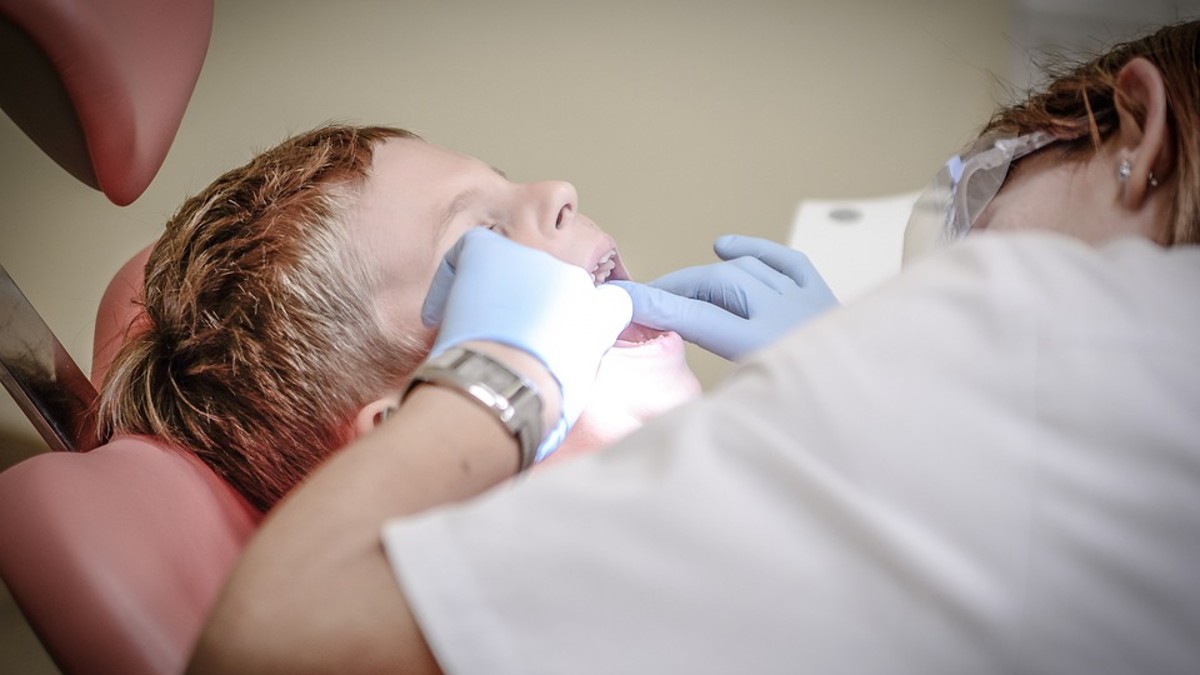
How
Does
Diabetes
Weaken
Your
Teeth?
The
link
between
diabetes
and
dental
health
is
complex
and
multifactorial.
Heart
disease,
comas,
blindness,
and
kidney
failure
are
all
well-known
effects
of
diabetes.
However,
very
few
people
are
aware
of
the
connection
between
oral
health
and
diabetes.
To
help
diabetic
patients
control
their
blood
sugar
levels
and
prevent
diabetes-related
tooth
and
gum
problems,
a
dentist-diabetologist
collaboration
is
required.
Diabetics
are
more
likely
to
have
dental
problems
for
the
following
reasons:
1.
High
sugar
levels
in
the
saliva
(like
in
diabetics)
are
a
breeding
ground
for
cavity-causing
bacteria.
Conversely,
ongoing
dental
infections
like
bleeding
gums
and
tooth
decay
can
raise
blood
sugar
levels
and
make
it
more
difficult
to
manage
diabetes.
2. Medication for diabetes lowers saliva production, causing dry mouth. Dry, stuffy nooks and crannies inside the mouth attract more plaque and worsen gum infections. In addition, the acidic foods and beverages you consume start eroding your teeth's enamel because your saliva does not wash them away.
3. Diabetes has an impact on blood vessels. They rapidly increase in size, thickness, and fragility. These vessels do not deliver blood as effectively as the regular ones do. This results in poor nutrition supply to the gums and teeth. As a result, your oral health is severely affected, making it more susceptible to infection.
The factors causing diabetes teeth and gum problems essentially form a triad. Research has shown that high blood sugar levels, poor oral hygiene, and a weakened immune system are key factors that contribute to dental problems in people with diabetes.
Diabetes,
Teeth
And
Gum
Problems:
Signs
You
Need
To
Notice
High
blood
sugar
levels
can
often
get
diagnosed
at
the
dental
clinic.
Diabetes
types
1
and
2
both
present
with
significant
dental
issues
that
can
be
alarming
and
can
lead
to
tooth
loss
if
left
untreated.
Let
us
explore
some
of
the
signs
and
symptoms
of
poor
oral
health
related
to
high
blood
sugar
levels:
Gum
infection
Gum
disease,
also
known
as
periodontitis,
is
a
common
dental
problem
in
diabetics.
The
culprit
is
the
bacterial
population
found
in
dental
plaque.
The
high
blood
sugar
in
the
saliva
and
the
dry
mouth
is
a
safe
haven
for
them.
These
bacteria
release
toxins
that
can
cause
gum
inflammation
and
swelling.
Over
time,
the
inflammation
may
cause
damage
to
the
bone
and
tissue
supporting
the
teeth,
which
could
lead
to
tooth
loss.
Periodontitis can present as follows:
- Soggy, enlarged, and bleeding gums
- There is teeth sensitivity to cold and sweet foods.
- A dull, boring jaw pain
- A salty taste, bad breath, and receding gum line
- Spacing and gaps between the teeth
Gum diseases are more common in diabetics because the disease can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
Cavities
Another
dental
issue
that
is
more
prevalent
in
diabetics
is
tooth
decay,
or
dental
caries,
simply
known
as
cavities.
High
blood
sugar
levels
result
in
a
dry
mouth,
which
allows
acidic
foods
to
erode
tooth
enamel.
Eroded
enamel
exposes
the
tooth
to
toxins
from
the
bacteria
that
cause
cavities.
Look out for the following symptoms:
- Dry mouth
- A burning sensation in the mouth
- Multiple dark spots on the tooth
- Cavities and holes in the tooth
- Toothache and sensitivity
- Small simple-like pus-filled abscesses
Tooth cavities can be very painful and can cause deadly infections in the head and neck region if left untreated.
Oral
infections
Oral
infections
are
also
more
common
in
people
with
diabetes.
People
with
diabetes
are
at
a
higher
risk
of
developing
thrush,
a
fungal
infection
that
can
cause
white
patches
in
the
mouth
and
a
sore
throat.
They
are
also
more
likely
to
develop
oral
herpes,
a
viral
infection
that
can
cause
painful
sores
on
the
lips
or
inside
the
mouth.
Can
poor
oral
health
lead
to
diabetes
-
here
are
a
few
ways
you
can
control
it
It's
crucial
for
diabetics
to
maintain
good
dental
health.
Here
are
some
pointers
to
help
you
keep
good
dental
health:
Keep
a
daily
glucose
log
and
take
the
prescribed
medications
as
directed.
The
market
is
flooded
with
reliable,
FDA-approved
blood
sugar
monitoring
equipment.
A
great
way
to
manage
your
sweet
tooth
is
to
use
sugar-free
sweet
alternatives.
You'll
soon
see
the
results
if
you
stop
indulging.
Reduce
blood
sugar
levels
Lowering
blood
sugar
levels
can
lower
the
likelihood
of
having
tooth
issues.
Regular
brushing
and
flossing
Good
oral
hygiene
can
help
reduce
plaque,
stop
gum
disease,
and
guard
against
tooth
decay.
Flossing
is
especially
important
to
clean
all
the
nooks
and
crevices
in
a
dry
diabetic
mouth.
Use
mouthwash
Mouthwash
can
help
reduce
the
bacteria
in
the
mouth
and
prevent
infections
all
day
long.
Moreover,
this
liquid
reaches
those
areas
where
the
toothbrush
wouldn't.
Quit
smoking
Smoking
can
increase
the
risk
of
gum
disease
and
oral
infections
by
drying
the
mouth
and
suppressing
the
blood
supply
to
the
gums.
It
is
a
potential
poison
for
the
gums.
Diet
Eat
fewer
foods
that
cause
blood
sugar
to
spike
and
drink
plenty
of
water.
Include
a
lot
of
foods
high
in
fibre,
like
salads
and
raw
fruits.
Hydrate
Dehydration
concentrates
the
blood,
resulting
in
a
rise
in
blood
sugar.
Additionally,
it
lessens
saliva
flow,
which
makes
the
gums
sore
and
enamel
more
prone
to
decay.
Conclusion
Maintaining
good
oral
health
ultimately
helps
you
control
your
diabetes
and
avoid
health
complications
linked
to
it.
Losing
teeth
due
to
poor
dental
health
will
make
it
more
difficult
for
you
to
follow
a
healthy
meal
plan,
which
is
essential
for
managing
diabetes.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












