Latest Updates
-
 Winter Care Guide: Expert Tips to Improve Your Child’s Immunity
Winter Care Guide: Expert Tips to Improve Your Child’s Immunity -
 The Celebrity Weddings That Took Us From “I’m Engaged” to “Just Married” In 2025
The Celebrity Weddings That Took Us From “I’m Engaged” to “Just Married” In 2025 -
 Rs 50,700 Jump in Gold Rate in India Over 4 Days in 24K/100gm; Silver Rate Today Continues Rally on Christmas, 25 December 2025: Check Latest Prices in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad With Gold, Silver Rate Prediction
Rs 50,700 Jump in Gold Rate in India Over 4 Days in 24K/100gm; Silver Rate Today Continues Rally on Christmas, 25 December 2025: Check Latest Prices in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad With Gold, Silver Rate Prediction -
 “67” Is Dictionary.com’s 2025 Word of the Year: The Viral Trend With No Meaning That Took Over the Internet
“67” Is Dictionary.com’s 2025 Word of the Year: The Viral Trend With No Meaning That Took Over the Internet -
 Bus Catches Fire After Collision With Lorry In Karnataka; At Least 10 Dead
Bus Catches Fire After Collision With Lorry In Karnataka; At Least 10 Dead -
 Skin Cycling, Glass Skin, and Sunscreen Stacking: The Internet’s Craziest Skincare Trends Explained
Skin Cycling, Glass Skin, and Sunscreen Stacking: The Internet’s Craziest Skincare Trends Explained -
 Post-Christmas Bloating Is Real: What Your Body Is Trying to Tell You
Post-Christmas Bloating Is Real: What Your Body Is Trying to Tell You -
 Atal Bihari Vajpayee Birthday 2025: Celebrating Good Governance Day in India
Atal Bihari Vajpayee Birthday 2025: Celebrating Good Governance Day in India -
 Think Twice This Christmas 2025: These Gifts Are A Total No For These Zodiac Signs
Think Twice This Christmas 2025: These Gifts Are A Total No For These Zodiac Signs -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 25, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 25, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
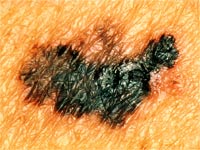
Skin Cancer Caused By A Protein
Cancer is one deadly disease that has taken many lives in the recent years and most people are getting more prone to cancer. In a recent study, it is said that for patients who are suffering from skin cancer is due to the unexpected protein of sun exposure.
The research also said that drugs can stop the halt of the tumor by blocking the protein for skin cancer patients. This form of cancer is also known as Cutaneous Melanoma is becoming quite common today and to treat patients with this disease is becoming difficult too.
In the study, it is said that severe sunburns at an early age raises a person"s risk of cutaneous melanoma or skin cancer , but surprisingly the way in which those burns lead to cancer has remained elusive.
Edward De Fabo, a research professor at the Tropical Medicine at George Washington University Medical Center in Washington, D.C, and other researchers are trying to find out new ways in treating cutaneous melanoma or skin cancer. He stated," We have been examining the pathway between ultraviolet (UV) rays and melanoma for over a decade. We ultimately want to figure out what goes wrong so that we can fix it."
In the year, 2004, Edward De Fabo and his team mates came to a suspicion that UV-B radiation, as opposed to UV-A, triggered melanoma. But as they studied further on this topic of Skin Cancer they found that UV-B causes white blood cells called macrophages to migrate higher in the skin of mice and release an immune protein, interferon-y and realized that Instead of protecting the body like most interferon proteins do, interferon-y allowed tumors to grow by preventing the body"s natural immune response. Edward De Fabo later reported saying that, "We didn"t expect to see interferon-y aiding the tumor, instead of killing cancerous cells".
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications