Latest Updates
-
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs -
 Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year
Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year
World Brain Tumour Day: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Glioblastoma?
World Brain Tumour Day is observed annually on 8 June. The day is marked to raise awareness and educate people about brain tumours. This day was initially taken by the German Brain Tumor Association and is now celebrated worldwide to raise awareness and educate people about the brain tumour.
Among the many deadly health issues and diseases, brain tumour is the tenth leading cause of morbidity in India.
The most common kind of malignant brain tumour in adults is glioblastoma. This is a kind of brain cancer. It grows and spreads very quickly. This ailment does not have a cure as of now, however, it can be treated to help ease the person of its symptoms. Such tumours can easily invade the normal brain tissues. This is possible because glioblastoma tumours are able to grow on their own by making their own blood supply.

Although brain cancers are not common, they do occur. Men are more likely to have brain cancer when compared to women. The chances of having brain cancer increases as one age.

What Is Glioblastoma?
Also known as glioblastoma multiforme, this cancer is considered to be the most aggressive kind of cancer of the brain. This is a high-grade tumour in the brain of adults. It develops from star-shaped glial cells and is considered to be a fast-growing glioma. It grows rapidly and can spread to the nearby brain tissues.

What Are The Causes?
Although the cause of glioblastoma is not clear, research has linked it to genetic disorders such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and neurofibromatosis. A previous radiation therapy could also play a role in the occurrence of such a brain tumour. The Glioblastoma cells are said to have more of genetic abnormalities when compared to other kinds of brain tumours. Reports of research studies claim that genetic mutations are responsible for the formation of this brain tumour.
Genetic mutation results in a cell breaking away from its usual growth routine and death cycle. This abnormal cell can create several copies of itself. These can then accumulate to form a tumour.

What Are The First Symptoms Of Glioblastoma?
As the tumour cells grow quickly, it is the pressure that leads to the first occurrence of the symptoms. Depending on the location of the tumour, there could be the following symptoms:
•
Trouble
thinking
and
learning
•
Vomiting
•
Seizures
•
Constant
headache
•
Mood
swings
•
Trouble
speaking
•
Blurred
vision
•
Loss
of
appetite
•
Change
in
personality
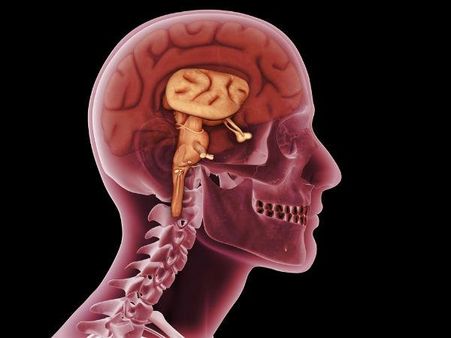
What Part Of The Brain Does Glioblastoma Affect?
Glioblastoma falls under the category of cancer that we refer to as astrocytoma. This kind of cancer is said to have its formation from star-shaped cells that are present in the brain. These cells are known as astrocytes. The cancer initiates from the cerebrum (the largest part of the brain). It is found in the cerebral hemispheres, mostly the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain.

How Is It Diagnosed And Treated?
You
need
to
approach
a
neurologist
to
get
the
proper
diagnosis
and
treatment.
Depending
on
your
symptoms,
you
might
need
to
get
an
MRI
or
a
CT
scan
done.
Once
diagnosed,
your
doctor
would
obtain
the
tumour
tissue
for
a
biopsy.
The
tissue
would
be
examined
by
a
neuropathologist.
This
is
essential
for
the
grading
of
the
tumour.
The goal of the treatment approach would be to slow the growth of the tumour.
•
The
first
form
of
treatment
is
surgery.
The
tumour
is
tried
to
be
removed
through
a
surgical
procedure.
In
case,
the
tumour
is
located
in
a
high-risk
position,
then
it
might
be
difficult
to
remove
it
completely.
•
Radiation
can
kill
the
leftover
tumour
cells
after
the
surgical
procedure.
In
case
some
part
of
the
tumour
cannot
be
removed,
then
at
least
radiation
can
slow
down
its
growth.
•
Chemotherapy
can
help
too.
The
most
common
chemotherapy
drug
used
is
temozolomide.
•
Electric
field
therapy
is
used
to
attack
the
tumour
cells,
without
affecting
the
normal
cells.
Electrodes
are
directly
attached
to
the
scalp.
The
device
used
is
known
as
Optune.
What Are The Chances Of Surviving Glioblastoma?
Treatments acquired can help ease out the symptoms of this ailment. It can also put the cancer into remission. However, glioblastoma has a chance of regrowing. When this occurs, doctors treat it through surgery and other forms of radiation and chemotherapy. According to research, the survival rates for glioblastoma are - 39.3 per cent for one year, 16.9 per cent for two years, 9.9 per cent for three years, 7.0 per cent for four years, 5.5 per cent for five years and 2.9 per cent for ten years.
The
lesser
the
age,
the
chances
are
better.
(When
the
survival
rate
is
39.3
per
cent
for
one
year,
it
means
that
39
people
out
of
the
100
people
diagnosed
with
glioblastoma
would
be
alive
after
one
year.)
Can Glioblastoma Spread To Other Organs?
A tumour that has initiated in the brain rarely spreads to the other organs of the body. However, the tumour can affect the central nervous system. Metastatic spread of this form of brain cancer outside the central nervous system is usually rare and hence when this form of brain cancer is detected, the doctor would most likely not recommend an examination of the other organs/parts of the body. It does not spread to other organs as it would be difficult for the tumour to penetrate blood vessels and reach other organs.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












