Latest Updates
-
 Mahayuti Sweeps Maharashtra Local Body Polls, BJP Emerges Largest Party
Mahayuti Sweeps Maharashtra Local Body Polls, BJP Emerges Largest Party -
 The World’s First Harry Potter-Themed Hotel Is All Set to Open In Europe
The World’s First Harry Potter-Themed Hotel Is All Set to Open In Europe -
 Dhurandhar 16 Days Collection | Dhurandhar Beats Jawan, Stree 2 | Dhurandhar 500cr | Dhurandhar Day 16 Collection | Dhurandhar Box Office Collection Day 17 Prediction (December 21, 2025) | Dhurandhar Third Weekend Collection Prediction | Dhurandhar Today Collection
Dhurandhar 16 Days Collection | Dhurandhar Beats Jawan, Stree 2 | Dhurandhar 500cr | Dhurandhar Day 16 Collection | Dhurandhar Box Office Collection Day 17 Prediction (December 21, 2025) | Dhurandhar Third Weekend Collection Prediction | Dhurandhar Today Collection -
 How to Dress Well This Holiday Season Without Overthinking It
How to Dress Well This Holiday Season Without Overthinking It -
 From Guava To Kiwi: Fruits to Have in Winters to Boost Your Immunity
From Guava To Kiwi: Fruits to Have in Winters to Boost Your Immunity -
 David Guetta Returns to Mumbai After 8 Years, Lights Up Sunburn Festival 2025
David Guetta Returns to Mumbai After 8 Years, Lights Up Sunburn Festival 2025 -
 How Homeopathic Remedies May Support Gut and Brain Health, Expert Explains
How Homeopathic Remedies May Support Gut and Brain Health, Expert Explains -
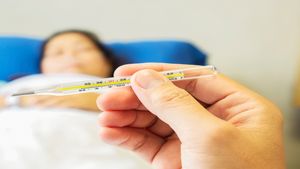 Why Viral Fevers Are Lasting Longer This Year: Expert Explains The Immunity Shift Post-COVID
Why Viral Fevers Are Lasting Longer This Year: Expert Explains The Immunity Shift Post-COVID -
 Rekha’s Timeless Wedding Season Style: 5 Things to Pick From Her Latest Look
Rekha’s Timeless Wedding Season Style: 5 Things to Pick From Her Latest Look -
 Gold Rate Today in India Flat, Silver Prices Jump to New High of Rs 2.14 Lakh: Check Latest Prices in Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Ahmedabad & Delhi
Gold Rate Today in India Flat, Silver Prices Jump to New High of Rs 2.14 Lakh: Check Latest Prices in Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Ahmedabad & Delhi
Sleep Disturbances Increase Inflammatory Disease Risk: Finds Study
Sleep disturbances and longer sleep duration are associated with increases in markers of inflammation, finds a new study.
Insufficient sleep is considered to be a public health epidemic by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
"Together with diet and physical activity, sleep health represents a third component in the promotion of health-span," said Michael Irwin from the University of California, Los Angeles, USA.
Common sleep disturbances, such as insomnia, have been associated with increased risk of inflammatory disease and mortality.
"Sleep disturbance or insomnia should be regarded as behavioural risk factors for inflammation, similar to the adverse effects of high fat diet or sedentary behaviour," Irwin added.

Inflammation causes a number of substances to increase in volume in the bloodstream, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Increased levels of these substances predict adverse health conditions, including cardiovascular events, hypertension and type 2 diabetes, said the paper published in the journal 'Biological Psychiatry'.
People with a normal sleep duration get 7-8 hours of shut-eye per night.
The findings showed that sleep disturbance, poor sleep quality or complaints of insomnia and long sleep duration, which is more than 8 hours, were associated with increased levels of CRP and IL-6.
Shorter sleep duration was associated with increased levels of CRP.
"It is important to highlight that both too much and too little sleep appear to be associated with inflammation, a process that contributes to depression as well as many medical illnesses," noted John Krystal, editor of the journal 'Biological Psychiatry'.
For the study, the team conducted a meta-analysis of 72 different articles for associations between sleep and inflammatory markers, which included over 50,000 participants from population-based and clinical studies.
Treatments targeting sleep behaviour could be a strategy for reversing the inflammation and reducing the risk of inflammatory illnesses, the researchers concluded.
Inputs from IANS
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












