Latest Updates
-
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs -
 Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year
Paush Amavasya 2025: Do These Most Powerful Rituals For Closure On The Final Amavasya Of The Year
Osteoarthritis (OA): Expert Shares Signs, Causes, Symptoms And Treatments
Called by many names like, wear-and-tear arthritis, degenerative arthritis, Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition that can cause pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the joints. Osteoarthritis can occur in any joint, but it is most commonly found in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Among a leading cause of disability, there are multiple reasons that cause Osteoarthritis one of which is the wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the joints. Cartilage is a tough, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, allowing them to glide smoothly over each other.
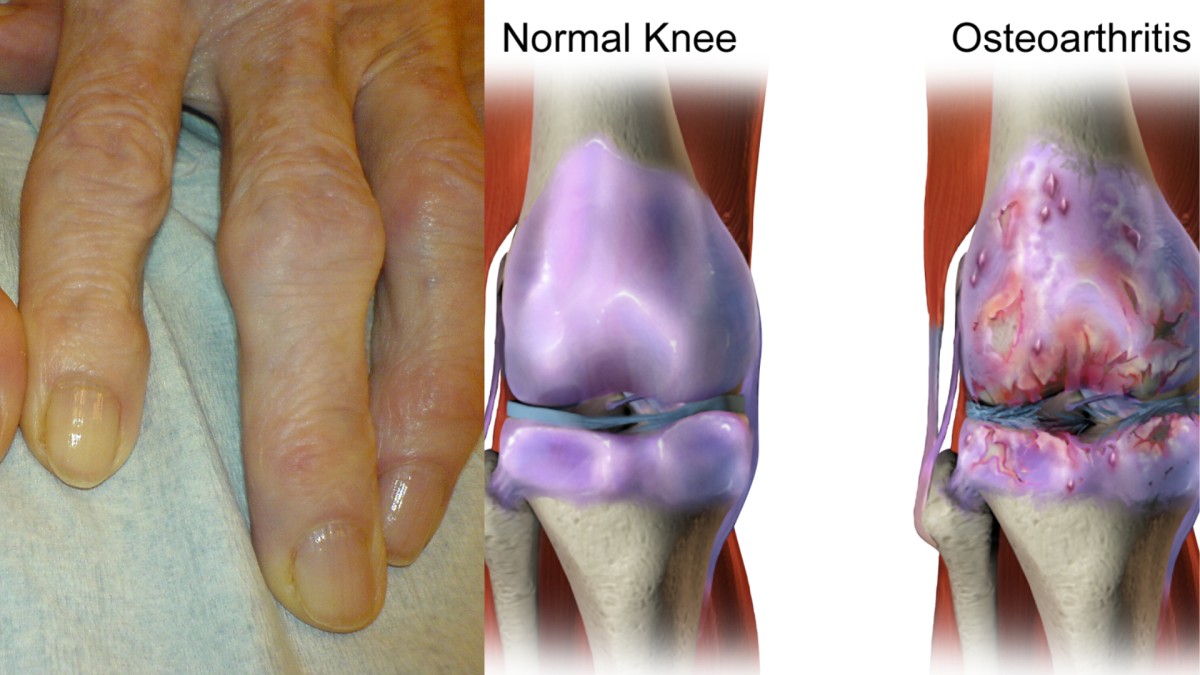
As we age, the cartilage in our joints usually become thin and damaged, leading to osteoarthritis. Other factors that can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis include:
Obesity:
Being
overweight
puts
extra
stress
on
the
joints,
which
can
accelerate
the
wear
and
tear
of
cartilage.
Injury:
Previous
joint
injuries
can
increase
the
risk
of
developing
post
traumatize
arthritis
later
in
life.
Genetics:
Genetic
predisposition
can
make
a
person
more
susceptible
to
developing
osteoarthritis.
Occupation:
Jobs
that
involve
repetitive
motions
or
heavy
lifting
can
increase
the
risk
of
developing
osteoarthritis.
The
symptoms
of
osteoarthritis
can
vary
depending
on
the
severity
of
the
disease
and
the
joint(s)
affected.
Some
common
symptoms
of
osteoarthritis
include:
Pain:
The
pain
associated
with
osteoarthritis
is
typically
described
as
a
deep
ache
in
the
joint
that
worsens
with
activity
and
improves
with
rest.
Stiffness:
Osteoarthritis
can
cause
stiffness
in
the
affected
joint,
especially
in
the
morning
or
after
prolonged
periods
of
inactivity.
Swelling:
The
joint
may
become
swollen
and
tender
to
the
touch.
Limited
mobility:
As
the
disease
progresses,
the
joint
may
become
less
mobile,
making
it
difficult
to
perform
daily
activities.
Joint
instability
due
to
muscle
weakness
can
lead
to
walking
difficulty
&
falls.
Osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and the patient's medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the disease. Blood tests are not typically used to diagnose osteoarthritis. Once the diagnosis is made treatment is usually required. Whole There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the symptoms of the disease.
Some
common
treatments
for
osteoarthritis
include:
Medications:
Over-the-counter
pain
relievers
such
as
acetaminophen
and
nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory
drugs
(NSAIDs)
can
help
relieve
pain
and
inflammation
in
the
affected
joint.
Physical
therapy:
Exercises
and
stretches
prescribed
by
a
physical
therapist
can
help
improve
mobility
and
reduce
pain.
Injections:
Corticosteroid
injections
into
the
affected
joint
can
help
reduce
inflammation
and
relieve
pain.
Surgery:
In
severe
cases,
joint
replacement
surgery
may
be
necessary
to
replace
the
damaged
joint
with
an
artificial
one.
While
there
is
no
surefire
way
to
prevent
osteoarthritis,
there
are
steps
that
can
be
taken
to
reduce
the
risk
of
developing
the
disease.
These
include:
Maintaining
a
healthy
weight:
Losing
excess
weight
can
reduce
the
stress
on
joints,
especially
those
in
the
hips,
knees,
and
spine.
Staying
active:
Regular
exercise
can
help
keep
joints
healthy
and
reduce
the
risk
of
injury.
Protecting
joints:
Avoiding
repetitive
abnormal
motions
and
using
proper
form
when
lifting
heavy
objects
can
help
protect
joints
from
damage.
Osteoarthritis is a common and chronic joint disease that can cause pain, stiffness, and inflammation. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the symptoms of the disease. Additionally, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis, including maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and protecting joints.
If
you
are
experiencing
joint
pain
or
stiffness,
it
is
important
to
speak
with
your
doctor
to
determine
the
cause
and
develop
an
appropriate
treatment
plan.
With
proper
management,
individuals
with
osteoarthritis
can
maintain
a
good
quality
of
life
and
continue
to
participate
in
daily
activities.
(The
article
has
been
contributed
by
Dr
Chetan
Jakaraddi,
Consultant
&
Surgeon
Joint
Replacement
and
Arthoscopy,
HCG
Hubli.)
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












