Latest Updates
-
 Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet
Purported Video of Muslim Mob Lynching & Hanging Hindu Youth In Bangladesh Shocks Internet -
 A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses
A Hotel on Wheels: Bihar Rolls Out Its First Luxury Caravan Buses -
 Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby
Bharti Singh-Haarsh Limbachiyaa Welcome Second Child, Gender: Couple Welcome Their Second Baby, Duo Overjoyed - Report | Bharti Singh Gives Birth To Second Baby Boy | Gender Of Bharti Singh Haarsh Limbachiyaa Second Baby -
 Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family
Bharti Singh Welcomes Second Son: Joyous News for the Comedian and Her Family -
 Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December
Gold & Silver Rates Today in India: 22K, 24K, 18K & MCX Prices Fall After Continuous Rally; Check Latest Gold Rates in Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad & Other Cities on 19 December -
 Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral
Nick Jonas Dancing to Dhurandhar’s “Shararat” Song Goes Viral -
 From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens
From Consciousness To Cosmos: Understanding Reality Through The Vedic Lens -
 The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather
The Sunscreen Confusion: Expert Explains How to Choose What Actually Works in Indian Weather -
 On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat
On Goa Liberation Day 2025, A Look At How Freedom Shaped Goa Into A Celebrity-Favourite Retreat -
 Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Daily Horoscope, Dec 19, 2025: Libra to Pisces; Astrological Prediction for all Zodiac Signs
Cellulitis: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
The primary function of the skin, the largest organ of the body, is to protect the body from infections. But sometimes the skin becomes infected when pathogens such as bacteria, virus, or fungus start attacking it. In this article, we will be discussing cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection that develops in the deep layers of the skin.
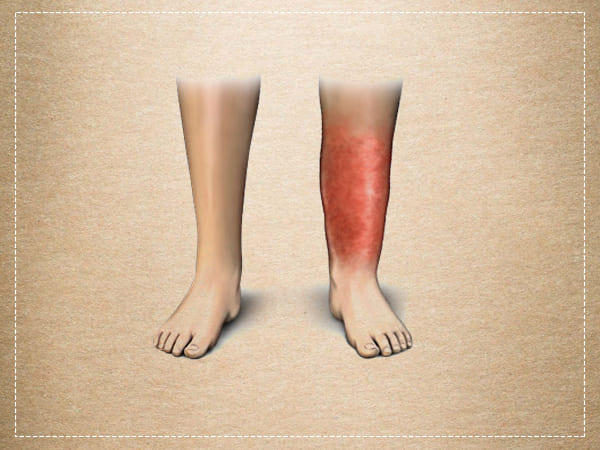
Image source: www.drugs.com
What Is Cellulitis [1]
Cellulitis is a common painful bacterial infection that usually affects the skin of the lower legs, but it can also occur on your face, arms or other parts of the body. The affected skin appears to be red and swollen and is quite painful and warm to the touch.
Cellulitis usually develops on the surface of the skin, but it may also affect the soft tissues underneath and spread to your lymph nodes and bloodstream.
What Causes Cellulitis [2]
Cellulitis occurs when certain types of bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus come in contact with the skin through a cut, scratch, or surgical wound. Animal bites can also cause cellulitis.
Types Of Cellulitis
- Breast cellulitis - It is a complication which can develop after radiation therapy for breast cancer [3] .
- Periorbital cellulitis - This type of cellulitis develops around the eyes [4] .
- Facial cellulitis - Facial cellulitis develops around the nose, cheeks and eyes [5] .
- Perianal cellulitis - This type of infection infects the anus and rectum [6] .
Symptoms Of Cellulitis
- Swelling and redness
- Tenderness and pain
- Warmth
- Fever
- Nausea
- Shivers
- Chills and cold sweats
- Fatigue
- A skin sore with pus
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Muscle aches
Risk Factors Of Cellulitis [7]
- Age - Cellulitis infection is more likely to occur during or after middle age.
- History - If you have had cellulitis before you have an 8-20% risk of getting it again.
- Obesity - People who are obese have an increased risk of cellulitis.
- Injury - An injury caused by a cut, burn, or fracture allows the entry of bacteria.
- Skin conditions - Eczema, athlete's foot and shingles cause tears on the skin which can make way for the bacteria.
- Weak immunity - People with diabetes, HIV/AIDS and leukaemia are susceptible to cellulitis.
- Lymphedema - It is a condition that causes swollen skin, which can crack and allow the bacteria to enter.
ALSO READ: Happy Birthday Milind Soman: Diet And Fitness Secrets Of The Supermodel
Complications Of Cellulitis
- It can damage the lymphatic drainage system and cause chronic swelling of the affected limb.
- It can lead to blood infection and sepsis.
- In rare cases, cellulitis can spread and infect other parts of the body, including the muscles, bones or heart valves.
When To See A Doctor
It's important to treat cellulitis early because it can spread easily throughout the body. If you notice a red, swollen, tender rash on the skin that's changing rapidly you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnosis Of Cellulitis [8]
According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, doctors diagnose cellulitis by examining the infected skin and ask questions like whether you have had a recent injury to your skin, any medical conditions you have and what medications you take.
Treatment Of Cellulitis [8]
Antibiotics are prescribed for 5 to 14 days for treating cellulitis. In most cases, after a few days, the symptoms disappear. If the infection is severe, you may need intravenous antibiotics. If your symptoms get worse, you may have to be hospitalized for a few days to ensure faster treatment.
Your doctor may also advise rest and might recommend you to elevate the affected area, to aid in faster recovery.
Prevention Of Cellulitis
- Avoid scratching an insect bite to prevent infection.
- Treat cuts, wounds, and grazes to lower the risk of infection.
- Keep your skin moisturised to prevents cracks in the skin.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- [1] Swartz, M. N. (2004). Cellulitis.New England Journal of Medicine,350(9), 904-912.
- [2] Spelman, D., Baddour, L. M., & Kaplan, S. L. (2017). Cellulitis and skin abscess: clinical manifestations and diagnosis, 1-150.
- [3] Staren, E. D., Klepac, S., Smith, A. P., Hartsell, W. F., Segretti, J., Witt, T. R., ... & Bines, S. D. (1996). The dilemma of delayed cellulitis after breast conservation therapy.Archives of Surgery,131(6), 651-654.
- [4] Weiss, A., Friendly, D., Eglin, K., Chang, M., & Gold, B. (1983). Bacterial periorbital and orbital cellulitis in childhood.
- [5] Rath, E., Skrede, S., Mylvaganam, H., & Bruun, T. (2018). Aetiology and clinical features of facial cellulitis: a prospective study.Infectious Diseases,50(1), 27-34.
- [6] Brook, I. (1998). Microbiology of perianal cellulitis in children: comparison of skin swabs and needle aspiration.International journal of dermatology,37(12), 922-924.
- [7] Björnsdóttir, S., Gottfredsson, M., Thórisdóttir, A. S., Gunnarsson, G. B., Rikardsdottir, H., Kristjánsson, M., & Hilmarsdóttir, I. (2005). Risk factors for acute cellulitis of the lower limb: a prospective case-control study.Clinical infectious diseases,41(10), 1416-1422.
- [8] Sullivan, T., & de Barra, E. (2018). Diagnosis and management of cellulitis.Clinical medicine (London, England),18(2), 160-163.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












